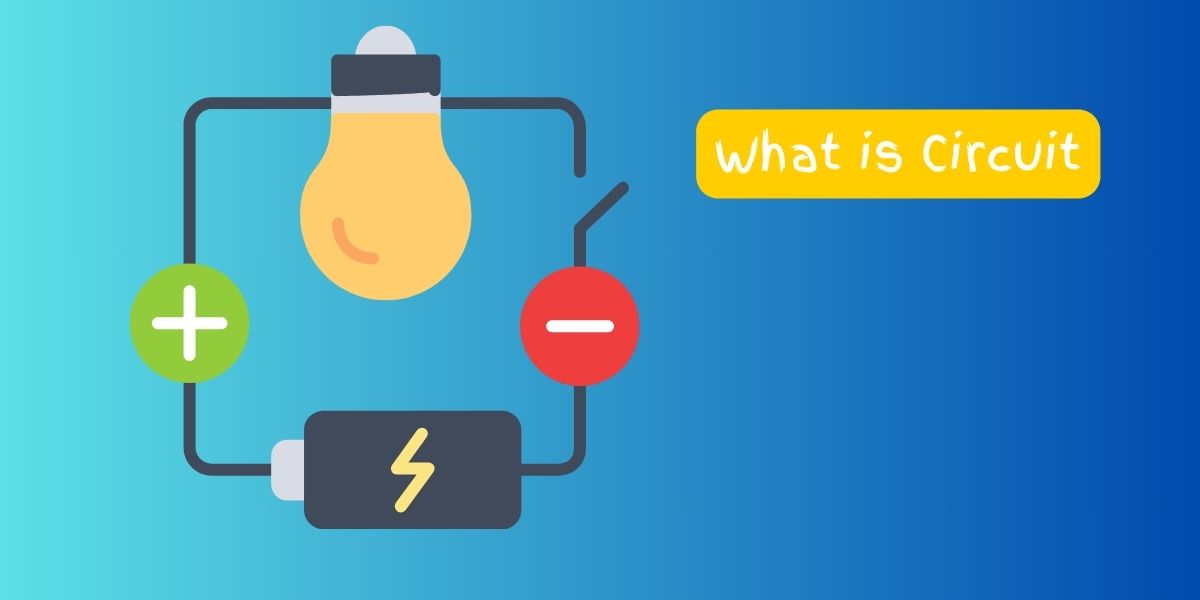
Circuit Analogy: The Water Pipe System
Imagine a circuit as a system of pipes that carries water from one place to another. Here’s how the analogy works:
- Water Source (Battery):
- Just like a battery provides electrical energy to a circuit, imagine a water tank or reservoir as the source of water in our analogy.
- Water Pipes (Wires):
- Wires in a circuit act like pipes that carry water from one place to another. They allow electricity to flow from the source (battery) to the components in the circuit.
- Components (Light Bulbs, Motors, etc.):
- Components in a circuit, such as light bulbs or motors, are like water-powered devices that perform tasks when water flows through them.
- For example, a light bulb lights up when electricity flows through it, just like a water-powered fountain sprays water when it receives water flow.
- Switch (On/Off Control):
- A switch in a circuit is like a valve or faucet in a water pipe system. It controls the flow of water (or electricity) through the circuit.
- When the switch is turned on, it allows water (or electricity) to flow through the circuit, activating the components. When it’s turned off, it stops the flow, and the components stop working.
- Open and Closed Circuits:
- An open circuit is like a broken pipe that prevents water from flowing. In an open circuit, electricity cannot flow, and the components do not work.
- A closed circuit is like a connected pipe system that allows water to flow freely. In a closed circuit, electricity can flow, and the components work as intended.
By using the water pipe system analogy, kids can visualize how electricity flows through a circuit and understand the roles of different components in completing the circuit and powering devices. It simplifies the concept of circuits and makes it relatable to everyday experiences with water systems.

No responses yet